Table of contents
- 1. What is Docker?
- 2. What are the advantages of using Docker container?
- 3. What are the important features of Docker?
- 4. What are the main drawbacks of Docker?
- 5. What is Docker image?
- 6. What is Docker Engine?
- 7. Explain Registries
- 8. What command should you run to see all running container in Docker?
- 9. Write the command to stop the docker container
- 10. What is the command to run the image as a container?
- Docker Interview Questions for Experienced Professionals
- 11. What are the common instruction in Dockerfile?
- 12. What is memory-swap flag?
- 13. Explain Docker Swarm?
- 14. How can you monitor the docker in production environments?
- 15. What the states of Docker container?
- 16. What is Docker hub?
- 17. What is Virtualization?
- 18. What is Hypervisor?
- 19. Explain Docker object labels
- 20. Write a Docker file to create and copy a directory and built it using python modules?
- 21. Where the docker volumes are stored?
- 22. List out some important advanced docker commands
- 23. How does communication happen between Docker client and Docker Daemon?
- 24. Explain Implementation method of Continuous Integration(CI) and Continues Development (CD) in Docker?
- 25. What are the command to control Docker with Systemd?
- 26. How to use JSON instead of YAML compose file?
- 27. What is the command you need to give to push the new image to Docker registry?
- 28. How to include code with copy/add or volumes?
- 29. Explain the process of scaling your Docker containers
- 30. What is the method for creating a Docker container?
- Docker Interview Questions for 5 Years Experience
- 31. What are the steps for the Docker container life cycle?
- 32. How can you run multiple containers using a single service?
- 33. What is CNM?
- 34. Does Docker offer support for IPV6?
- 35. Can you lose data when the container exits?
- 36. What are a different kind of volume mount types available in Docker?
- 37. How to configure the default logging driver under Docker?
- 38. Explain Docker Trusted Registry?
- 39. What are Docker Namespaces?
- 40. What are the three components of Docker Architecture
- 41. What is client?
- 42. What is the purpose of Docker_Host?
- 43. How do I run multiple copies of Compose file on the same host?
- Docker Interview
1. What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source lightweight containerization technology. It has gained widespread popularity in the cloud and application packaging world. It allows you to automate the deployment of applications in lightweight and portable containers.
2. What are the advantages of using Docker container?
Here, are a major advantage of using Docker.
Offers an efficient and easy initial set up
Allows you to describe your application lifecycle in detail
Simple configuration and interacts with Docker Compose.
Documentation provides every bit of information.
3. What are the important features of Docker?
Here are the essential features of Docker:
Easy Modeling
Version control
Placement/Affinity
Application Agility
Developer Productivity
Operational Efficiencies
T
4. What are the main drawbacks of Docker?
Some notable drawbacks of Docker are:
Doesn’t provide a storage option
Offer a poor monitoring option.
No automatic rescheduling of inactive Nodes
Complicated automatic horizontal scaling set up
5. What is Docker image?
The Docker image help to create Docker containers. You can create the Docker image with the build command. Due to this, it creates a container that starts when it begins to run. Every docker images are stored in the Docker registry.
6. What is Docker Engine?
Docker daemon or Docker engine represents the server. The docker daemon and the clients should be run on the same or remote host, which can communicate through command-line client binary and full RESTful API.
7. Explain Registries
There are two types of registry is
Public Registry
Private Registry
Docker’s public registry is called Docker hub, which allows you to store images privately. In Docker hub, you can store millions of images.
8. What command should you run to see all running container in Docker?
$ docker ps
9. Write the command to stop the docker container
$ sudo docker stop container name
10. What is the command to run the image as a container?
$ sudo docker run -i -t alpine /bin/bash
Docker Interview Questions for Experienced Professionals
11. What are the common instruction in Dockerfile?
The common instruction in Dockerfile are: FROM, LABEL, RUN, and CMD.
12. What is memory-swap flag?
Memory-swap is a modified flag that only has meaning if- memory is also set. Swap allows the container to write express memory requirements to disk when the container has exhausted all the RAM which is available to it.
13. Explain Docker Swarm?
Docker Swarm is native gathering for docker which helps you to a group of Docker hosts into a single and virtual docker host. It offers the standard docker application program interface.
14. How can you monitor the docker in production environments?
Docker states and Docker Events are used to monitoring docker in the production environment.
15. What the states of Docker container?
Important states of Docker container are:
Running
Paused
Restarting
Exited
16. What is Docker hub?
Docker hub is a cloud-based registry that which helps you to link to code repositories. It allows you to build, test, store your image in Docker cloud. You can also deploy the image to your host with the help of Docker hub.
17. What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is a method of logically dividing mainframes to allow multiple applications to run simultaneously.
However, this scenario changed when companies and open source communities were able to offer a method of handling privileged instructions. It allows multiple OS to run simultaneously on a single x86 based system.
18. What is Hypervisor?
The hypervisor allows you to create a virtual environment in which the guest virtual machines operate. It controls the guest systems and checks if the resources are allocated to the guests as necessary.
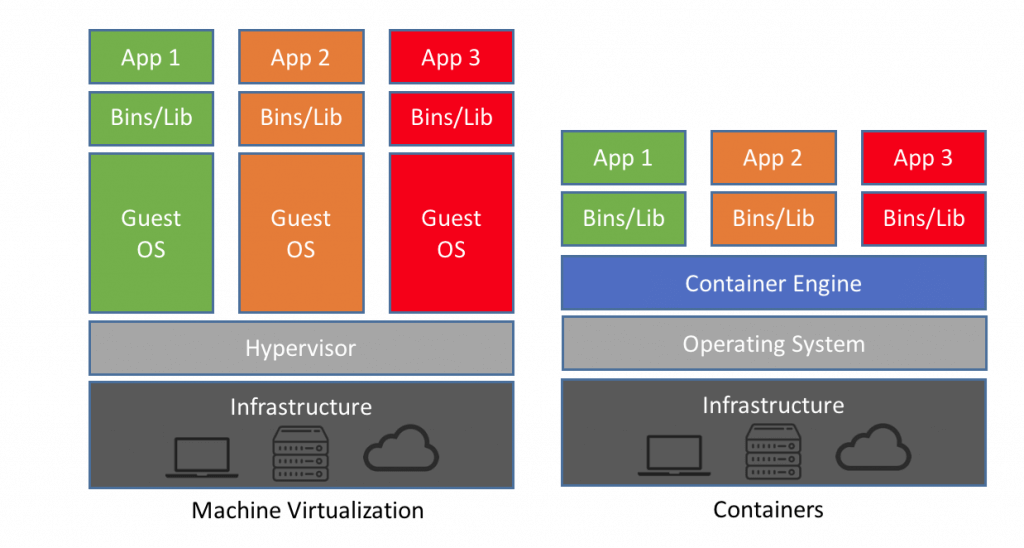
Virtualization in Docker vs Hypervisor
19. Explain Docker object labels
Docker object labels is a method for applying metadata to docker objects including, images, containers, volumes, network, swam nodes, and services.
20. Write a Docker file to create and copy a directory and built it using python modules?
FROM pyhton:2.7-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
docker build –tag
21. Where the docker volumes are stored?
You need to navigate:
/var/lib/docker/volumes
22. List out some important advanced docker commands
| Command | Description |
| docker info | Information Command |
| docker pull | Download an image |
| docker stats | Container information |
| Docker images | List of images downloaded |
23. How does communication happen between Docker client and Docker Daemon?
You can communicate between Docker client and Docker Daemon with the combination of Rest API, socket.IO, and TCP.
24. Explain Implementation method of Continuous Integration(CI) and Continues Development (CD) in Docker?
You need to do the following things:
Runs Jenkins on docker
You can run integration tests in Jenkins using docker-compose
25. What are the command to control Docker with Systemd?
systemctl start/stop docker
service docker start/stop
26. How to use JSON instead of YAML compose file?
docker-compose -f docker-compose.json up
27. What is the command you need to give to push the new image to Docker registry?
docker push myorg/img
28. How to include code with copy/add or volumes?
In docker file, we need to use COPY or ADD directive. This is useful to relocate code. However, we should use a volume if we want to make changes.
29. Explain the process of scaling your Docker containers
The Docker containers can be scaled to any level starting from a few hundred to even thousands or millions of containers. The only condition for this is that the containers need the memory and the OS at all times, and there should not be a constraint when the Docker is getting scaled.
30. What is the method for creating a Docker container?
You can use any of the specific Docker images for creating a Docker container using the below command.
docker run -t -i command name
This command not only creates the container but also start it for you.
Docker Interview Questions for 5 Years Experience
31. What are the steps for the Docker container life cycle?
Below are the steps for Docker life cycle:
Build
Pull
Run
32. How can you run multiple containers using a single service?
By using docker-compose, you can run multiple containers using a single service. All docker-compose files uses yaml language.
33. What is CNM?
CNM stands for Container Networking Model. It is a standard or specification from Docker, Inc. that forms the basis of container networking in a Docker environment. This docker’s approach provides container networking with support for multiple network drivers.
34. Does Docker offer support for IPV6?
Yes, Docker provides support IPv6. IPv6 networking is supported only on Docker daemons runs on Linux hosts. However, if you want to enable IPv6 support in the Docker daemon, you need to modify /etc/docker/daemon.json and set the ipv6 key to true.
35. Can you lose data when the container exits?
No, any data that your application writes to disk get stored in container. The file system for the contain persists even after the container halts.
36. What are a different kind of volume mount types available in Docker?
Bind mounts- It can be stored anywhere on the host system
37. How to configure the default logging driver under Docker?
To configure the Docker daemon to default to a specific logging driver. You need to set the value of log-driver to the name of the logging drive the daemon.jason.fie.
38. Explain Docker Trusted Registry?
Docker Trusted Registry is the enterprise-grade image storage toll for Docker. You should install it after your firewall so that you can securely manage the Docker images you use in your applications.
39. What are Docker Namespaces?
The Namespace in Docker is a technique which offers isolated workspaces called the Container. Namespaces also offer a layer of isolation for the Docker containers.
40. What are the three components of Docker Architecture
Client
Docker-Host
Registry
41. What is client?
Docker provides Command Line Interface tools to the client to interact with Docker daemon.
42. What is the purpose of Docker_Host?
It contains container, images, and Docker daemon. It offers a complete environment to execute and run your application.
43. How do I run multiple copies of Compose file on the same host?
Compose uses the project name which allows you to create unique identifiers for all of a project’s containers and other resources. To run multiple copies of a project, set a custom project name using the -a command-line option or using COMPOSE_PROJECT_NAME environment variable.
Docker Interview
1. Difference between an Image, Container, and Engine:
Image: A Docker image is a template containing all the necessary files and configurations required to create a container. It includes the application code, runtime, libraries, dependencies, and other settings.
Container: A Docker container is an instance of a Docker image. It is a lightweight, runnable environment that encapsulates the application and its dependencies, allowing it to run consistently across different environments.
Engine: The Docker Engine is the core component responsible for building, running, and managing Docker containers. It consists of the Docker daemon, REST API, and command-line interface (CLI).
2. Difference between the Docker command COPY vs ADD:
COPY: Used in Dockerfile to copy files or directories from the host machine into the container. It is straightforward and ideal for copying local files into the container.
ADD: Similar to COPY but with additional features. It can handle URLs, unpack compressed files, and supports automatic extraction of tarred resources during copy. However, it's recommended to use COPY for simple file copying.
3. Difference between the Docker command CMD vs RUN:
RUN: Executes commands during the image build process to install packages, run installations, or set up the environment. It creates new image layers.
CMD: Defines the default command to be executed when a container starts. It can be overridden by providing a command when starting the container.
4. How to reduce the size of the Docker image:
Use minimal base images like Alpine Linux.
Combine multiple commands into a single RUN instruction to reduce image layers.
Clean up unnecessary files and dependencies after each installation step.
Use .dockerignore file to exclude unwanted files from being added to the image.
5. Why and when to use Docker:
Docker offers consistent environments for development, testing, and deployment.
Simplifies application deployment across different environments.
Encourages microservices architecture and enables container orchestration.
6. Explain Docker components and their interaction:
Docker Engine (daemon, REST API, CLI)
Docker Images (templates)
Docker Containers (running instances of images)
Docker Compose (orchestration tool)
Dockerfile (defines image configurations)

